广东白云学院创建于1989年,是教育部批准成立的全日制普通本科院校。学校位于广州市白云区,拥有江高和钟落潭两个校区,以本科教育为主,目前设有61个...
2025-08-13 58 广东白云学院学费 广东白云学院是公办还是民办 广东白云学院录取通知书
广东白云学院创建于1989年,是教育部批准成立的全日制普通本科院校。学校位于广州市白云区,拥有江高和钟落潭两个校区,以本科教育为主,目前设有57个本科专业,覆盖工学、管理学、艺术学、理学、经济学、文学、法学、教育学等学科,拥有省级重点学科、省级科研平台、博士工作站以及众多一流专业与课程,荣获广东省教学成果奖一等奖、二等奖、科研成果奖等一大批奖项。为实现高质量、创新型、集群化、数字化发展需要,更好地服务粤港澳大湾区特别是广东省经济社会发展,建设应用学科优势突出、产教融合特色鲜明的高水平应用型大学,特面向社会招聘优秀人才加盟。
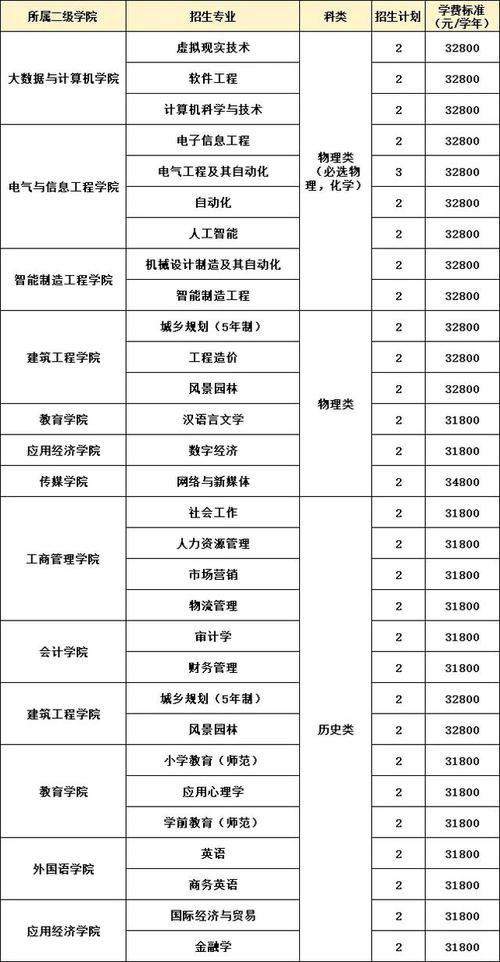
一、岗位职责
1.整理相关部门人力资源管理信息化需求,参与人资各业务流程的信息化建设,推进系统的运行及使用,受理运维需求;

2.建设、维护人事处现有网站和人事信息系统,录入人资基础数据,检查人力资源管理基础数据的准确性、完整性和规范性;
3.协助推进学校组织架构管理、职位职级体系管理、薪酬管理、人员编制优化及劳动效率提升;
4.利用系统数据为学校人力资源管理决策提供支持,按要求完成各类数据统计、维护与上报工作,并保证数据准确;
5.负责领导交办的其他事项。
二、任职要求
1.信息管理与信息系统、人力资源管理、劳动与社会保障、工商管理、统计学等相关专业硕士研究生;
2.熟悉人力资源管理流程,理解人力资源管理业务需求;具有较强的用户思维和业务敏感度,数据分析能力强,熟练使用word、excel、ppt等办公软件;熟悉高校人力资源管理或市场主流人力资源管理系统者优先;
3.具有较好的沟通协调能力,责任心强,工作积极主动,拥有较强的分析和解决问题能力,写作能力好。
三、待遇
待遇面议。
四、应聘方式
登录广东白云学院人事处网站(http://rlzy.baiyunu.edu.cn)填写《广东白云学院应聘人员登记表》(附件下载),发送至人事处电子信箱:rsc@baiyunu.edu.cn,邮件主题请注明:应聘岗位+学历+职称+姓名+今日招聘网jrzp.com,合则约见。【快捷投递:点击下方“立即投递/投递简历”,即刻进行职位报名】
联系地址:广州市白云区钟落潭镇九佛西路280号广东白云学院人事处
联系电话:020-36093948
学院网址:http://www.baiyunu.edu.cn
联系人:张老师魏老师
标签: 广东白云学院是公办还是民办 广东白云学院教务管理系统 广东白云学院录取分数线
相关文章
广东白云学院创建于1989年,是教育部批准成立的全日制普通本科院校。学校位于广州市白云区,拥有江高和钟落潭两个校区,以本科教育为主,目前设有61个...
2025-08-13 58 广东白云学院学费 广东白云学院是公办还是民办 广东白云学院录取通知书
广东白云学院创建于1989年,是教育部批准成立的全日制普通本科院校。学校位于广州市白云区,拥有江高和钟落潭两个校区,以本科教育为主,目前...
2025-08-13 58 广东白云学院是公办还是民办 广东白云学院2025年录取分数线 广东白云学院在哪
广东白云学院创建于1989年,是教育部批准成立的全日制普通本科院校。学校位于广州市白云区,拥有江高和钟落潭两个校区,以本科教育为主,目前设有˂span...
2025-08-08 54 广东白云学院是一本还是二本 广东白云学院教务管理系统 广东白云学院录取通知书
发表评论